

The attenuation by relative channel adds to that due to distance and the effects of obstacles.

Attenuation by channel spacing for 20 MHz transmitters : 3 Channel separation: However, the exact spacing required when the transmitters are not colocated depends on the protocol, the data rate selected, the distances and the electromagnetic environment where the equipment is used.
FREEBAND FREQUENCIES TO AVOID FULL
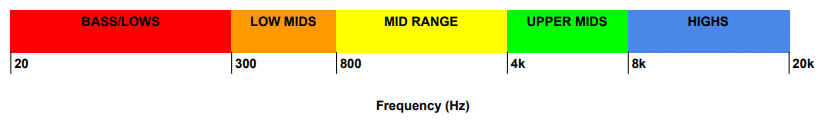
This guardband is mainly used to accommodate older routers with modem chipsets prone to full channel occupancy, as most modern WiFi modems are not prone to excessive channel occupancy.Įuropean Wi-Fi channel availability permits square frequency reuse patterns The remaining 2 MHz gap is used as a guard band to allow sufficient attenuation along the edge channels. To guarantee no interference in any circumstances the Wi-Fi protocol requires 16.25 to 22 MHz of channel separation (as shown below). Security features of WPA have included stronger protections and new security practices as the security landscape has changed over time. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a family of technologies created to protect information moving across Wi-Fi networks and includes solutions for personal and enterprise networks. At close range, some versions of Wi-Fi, running on suitable hardware, can achieve speeds of over 1 Gbit/s.Īnyone within range with a wireless network interface controller can attempt to access a network because of this, Wi-Fi is more vulnerable to attack (called eavesdropping) than wired networks. Many common materials absorb or reflect them, which further restricts range, but can tend to help minimise interference between different networks in crowded environments. These wavelengths work best for line-of-sight. Each channel can be time-shared by multiple networks. Wi-Fi most commonly uses the 2.4 gigahertz (12 cm) UHF and 5.8 gigahertz (5 cm) SHF ISM radio bands these bands are subdivided into multiple channels.
Hotspot coverage can be as small as a single room with walls that block radio waves, or as large as many square kilometres achieved by using multiple overlapping access points.ĭifferent versions of Wi-Fi exist, with different ranges, radio bands and speeds. Such an access point (or hotspot) has a range of about 20 meters (66 feet) indoors and a greater range outdoors. Wi-Fi compatible devices can connect to the Internet via a WLAN and a wireless access point. ĭevices that can use Wi-Fi technologies include desktops and laptops, video game consoles, smartphones and tablets, smart TVs, digital audio players, cars and modern printers. Wi‑Fi is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term Wi-Fi Certified to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. Wi-Fi ( / ˈ w aɪ f aɪ/) is technology for radio wireless local area networking of devices based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. Personal computers, gaming consoles, televisions, printers, mobile phones This technology was designed to ward off eavesdroppers, but the phone will change channels at random, leaving no Wi-Fi channel safe from phone interference. The last will sometimes not be successful, as numerous cordless phones use a feature called Digital Spread Spectrum.
Main articles: Cordless telephone and Baby monitor


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
